Hearing loss affects millions of Americans, yet not all types of hearing loss are the same. Understanding the difference between conductive vs. sensorineural hearing loss is essential for choosing the right treatment, technology, and support. Both conditions reduce your ability to hear clearly, but the causes, symptoms, and solutions vary. This guide will help you understand what makes each type unique, how they are diagnosed, and what treatment options exist today. By the end, you will know what steps to take if you or a loved one faces hearing challenges.
How Hearing Works: The Pathway of Sound
To appreciate how different types of hearing loss occur, it helps to understand how sound travels through the ear. Sound waves enter through the outer ear, travel down the ear canal, and strike the eardrum. The eardrum vibrates, setting the middle ear bones (the ossicles) in motion. These bones amplify sound and pass it into the cochlea, a fluid-filled structure in the inner ear lined with delicate hair cells. These hair cells convert vibrations into electrical signals that travel along the auditory nerve to the brain, where sound is interpreted.
Any disruption along this pathway can result in hearing loss. Conductive loss involves the outer or middle ear, where sound has trouble reaching the inner ear. Sensorineural loss occurs when the inner ear or auditory nerve is damaged. Mixed hearing loss combines both issues. Knowing which type you have is the key to effective treatment.
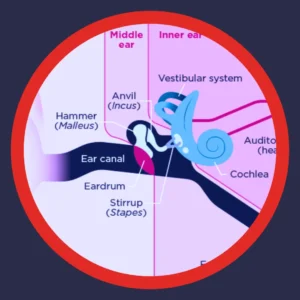
What Is Conductive Hearing Loss?
Conductive hearing loss happens when something blocks or reduces the sound from reaching the inner ear. With this type of loss, sound may seem muffled or quieter, but clarity is often preserved once the volume is increased.
Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss can result from conditions affecting the outer or middle ear. Common causes include:
- Earwax impaction that blocks the ear canal.
- Ear infections, including swimmer’s ear or middle ear infections.
- Perforated eardrum, caused by injury, trauma, or infection.
- Fluid in the middle ear, often seen in children after colds.
- Abnormal bone growths, such as exostoses or osteomas in the ear canal.
- Otosclerosis, a stiffening of the stapes bone.
- Cholesteatoma, a growth in the middle ear that damages tissue.
Some causes, like wax impaction or infections, are temporary and treatable. Others, like otosclerosis, may be permanent and require specialized care.
Symptoms of Conductive Hearing Loss
People with conductive hearing loss often report:
- Reduced loudness of sounds.
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
- Difficulty hearing on the phone.
- Pain or drainage in cases of infection.
- An unusual awareness of their own voice.
These symptoms can vary depending on whether the cause is temporary or permanent.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with a case history and an ear examination using an otoscope. Tympanometry may measure middle ear pressure, while an audiogram compares air conduction to bone conduction. A clear air-bone gap usually indicates conductive loss.
Treatment Options
Unlike sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss can often be corrected medically or surgically. Treatments include:
- Removal of earwax or foreign objects.
- Antibiotics for infections.
- Surgery for eardrum repair or ossicular chain reconstruction.
- Stapedectomy for otosclerosis.
If medical treatment is not possible or only partially effective, hearing aids or bone conduction devices can improve hearing. Bone conduction technology bypasses the blocked outer or middle ear by transmitting sound vibrations directly through the skull to the inner ear.
What Is Sensorineural Hearing Loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) occurs when there is damage to the inner ear’s hair cells or the auditory nerve. This is the most common type of permanent hearing loss and affects clarity rather than loudness. People with SNHL often say, “I can hear people talking, but I can’t understand them.”
Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Causes of SNHL include:
- Aging (presbycusis), the most common cause.
- Noise exposure, including work environments, concerts, or headphones.
- Genetics, which may predispose someone to early hearing loss.
- Viral or bacterial infections, such as mumps or meningitis.
- Medical conditions, including diabetes and heart disease.
- Ototoxic medications, such as certain chemotherapy drugs or antibiotics.
- Head trauma or concussions.
- Meniere’s disease, which also causes vertigo and tinnitus.
Research confirms that sensorineural damage often results from inner ear lesions. This highlights the need for early intervention and careful diagnosis.
Symptoms of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Symptoms may include:
- Difficulty hearing in noisy environments.
- Trouble following group conversations.
- High-pitched voices sound faint.
- Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears.
- Speech sounds seem unclear or distorted.
- A perception that noises are too loud or harsh.
Diagnosis
An audiogram is the main diagnostic tool. It measures thresholds across frequencies and checks speech recognition. Sensorineural loss usually shows a sloping curve on the chart, especially at higher frequencies.
Treatment Options
There is no medical cure for SNHL, but treatment can significantly improve communication. Options include:
- Hearing aids, which amplify sound and enhance speech clarity.
- Digital features such as directional microphones and noise reduction.
- Powerful behind-the-ear models for severe loss.
- Cochlear implants for those who gain little benefit from hearing aids.
Hearing aids are the first line of treatment for most people with SNHL. Cochlear implants may be considered when conventional aids do not provide enough benefit.

Mixed Hearing Loss: A Combination of Challenges
Mixed hearing loss combines features of both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Someone may have an infection or blockage along with permanent inner ear damage.
Causes of Mixed Hearing Loss
- Head trauma that affects both the middle and inner ear.
- Long-standing conductive issues combined with age-related SNHL.
- Temporary conductive loss layered on top of permanent sensorineural loss.
Treatment Options
Treatment usually starts with addressing the conductive component, such as clearing wax or treating an infection. Then amplification is provided through traditional hearing aids or bone conduction devices, depending on the individual’s needs.
Sudden Hearing Loss Needs Urgency
Not all hearing loss develops gradually. In some cases, changes in hearing occur suddenly, over a period of hours or days. This condition, known as sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL), is considered a medical emergency. The sooner you seek help, the better your chances of restoring some or all of your hearing.
Many people ignore sudden changes, assuming the problem is caused by allergies, wax buildup, or fluid in the ear. While those issues can sometimes cause conductive hearing loss, true SSHL originates in the inner ear or auditory nerve. Waiting to see if it clears on its own can cost valuable recovery time. Research shows that treatment within the first two weeks offers the best chance for improvement, and ideally, evaluation should happen within 48 hours.
Symptoms of SSHL can include:
- Hearing loss in one ear that appears overnight or within a few days.
- A sensation of fullness or pressure in the affected ear.
- Ringing or buzzing (tinnitus).
- Dizziness or balance problems that accompany hearing changes.
If you experience any of these symptoms, you should not delay. A hearing care provider will perform an ear examination to rule out conductive causes, such as wax or infection, and then conduct a full hearing test. An audiogram will confirm whether the loss is sensorineural in nature. Depending on the diagnosis, urgent treatments — often involving corticosteroids — may be prescribed to reduce inner ear inflammation and improve outcomes.
Equally important, a professional evaluation ensures that other serious conditions are not missed. Some inner ear tumors or vascular issues can present with sudden hearing changes, so comprehensive testing and medical referral, when necessary, are critical.
The key message is simple: sudden hearing loss is never normal and never something to ignore. If your hearing drops unexpectedly, treat it as an emergency. Contact a licensed provider immediately so you can begin treatment without delay.
Conductive vs. Sensorineural Hearing Loss Chart
|
Feature |
Conductive Hearing Loss |
Sensorineural Hearing Loss |
Mixed Hearing Loss |
Sudden Hearing Loss |
|
Location |
Outer or middle ear |
Inner ear or auditory nerve |
Both outer/middle and inner ear |
Usually inner ear or auditory nerve |
|
Main Issue |
Sound blocked before reaching inner ear |
Damage to hair cells or nerve pathways |
Combination of blockage and inner ear/nerve damage |
Rapid, unexplained inner ear or nerve damage |
|
Typical Causes |
Wax impaction, fluid, infection, perforated eardrum, otosclerosis |
Aging, noise, genetics, ototoxic drugs, inner ear disease |
Trauma, long-term conductive issues with age-related loss, blast injuries |
Viral infections, vascular events, autoimmune disease, sometimes unknown |
|
Symptoms |
Reduced loudness, ear fullness, clearer with volume increase |
Muffled or distorted speech, tinnitus, poor clarity in noise |
Combination of loudness reduction and clarity loss |
Sudden drop in hearing in one ear, tinnitus, ear fullness, dizziness |
|
Diagnosis |
Air-bone gap on audiogram, visible ear issues |
Sloping audiogram, poor speech understanding |
Both air-bone gap and inner ear pattern |
Audiogram showing sudden sensorineural loss, urgent exam needed |
|
Treatment |
Medical or surgical correction, hearing aids, bone conduction devices |
Hearing aids, cochlear implants, no medical cure |
Combination of medical treatment and hearing devices |
Immediate medical treatment (often steroids), followed by hearing aids if permanent |
|
Reversibility |
Often temporary or treatable |
Usually permanent |
Partially reversible depending on cause |
Sometimes reversible if treated quickly |
Modern Treatment Solutions
Treating hearing loss today involves much more than just making sounds louder. Advances in hearing care technology have created powerful solutions that improve clarity, reduce background noise, and even connect directly to your favorite devices. While some conductive hearing loss can be corrected medically or surgically, most people with hearing loss benefit from hearing aids or other supportive technology.
Hearing Aids: The Cornerstone of Care
Hearing aids remain the most effective treatment for both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. They are designed to restore clarity, not just volume. Modern digital processors allow your provider to program hearing aids precisely to your unique hearing profile, delivering customized results.
For people with advanced needs, the best hearing aids for severe hearing loss provide high power while still keeping speech natural. These devices are built to handle more challenging levels of hearing loss without sacrificing sound quality.
Hearing aids now include remarkable features that make life easier and communication more enjoyable. Directional microphones can zero in on the person you want to hear. Adaptive noise reduction helps you stay comfortable in busy places. Some models even detect environments automatically and adjust settings on their own. You can read more about the amazing features available in hearing aids today to see how far technology has advanced.
Rechargeability has also simplified daily life. Rechargeable hearing aids make daily life easier by removing the need for disposable batteries. Most offer all-day use with just a few hours of charging, and protective cases keep devices safe while doubling as chargers.
Comparing Hearing Aid Technology Levels
Not all hearing aids are the same. Technology levels vary, giving patients options that balance features with budget:
- Essential Technology: Covers the basics, amplifies sound, and helps with one-on-one conversations. Best for quiet lifestyles or those who spend most of their time at home.
- Mid-Level Technology: Adds adaptive noise reduction, directional microphones, and multiple listening programs. A good fit for people who socialize, attend group events, or dine out frequently.
- Premium Technology: Offers the most advanced features, including artificial intelligence, Bluetooth connectivity, automatic scene detection, and enhanced speech processing in noise. Ideal for active lifestyles, work settings, and those who want top performance in every environment.
Your hearing care provider can help determine which level fits your lifestyle, communication needs, and budget. Choosing the right technology ensures you get the most out of your investment.
Bone Conduction Devices
For people with conductive hearing loss that cannot be corrected medically, bone conduction devices offer an effective alternative. These devices bypass the outer and middle ear by transmitting sound vibrations through the bones of the skull directly to the cochlea. They are helpful for patients with chronic infections, ear canal malformations, or single-sided deafness. Options include external headband-style systems as well as implantable devices.
Cochlear Implants
When hearing aids are not enough, cochlear implants can provide another path forward. These devices are surgically implanted and bypass damaged hair cells by directly stimulating the auditory nerve. While not everyone is a candidate, cochlear implants have transformed communication for people with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss who no longer benefit from conventional amplification.
Assistive Listening Devices
Hearing aids can be paired with accessories to enhance listening in specific situations. Remote microphones improve clarity in classrooms or large group meetings. TV streamers deliver crisp dialogue straight to your hearing aids. Loop systems in theaters and churches connect directly to compatible devices for a seamless listening experience. You can explore additional supportive options in our shop to find tools that match your daily life.
Insurance and Medicare Considerations
Cost is a concern for many families, but options exist. Insurance coverage varies by plan, and Medicare has unique rules. Understanding your benefits helps you plan confidently. Our guide to Medicare hearing aids coverage explains what you need to know, from current coverage limits to ways you can maximize support.
Lifestyle and Communication Strategies
Technology is powerful, but communication strategies also make a difference. Adopting simple habits helps reduce listening fatigue and frustration.
- Face the person speaking.
- Reduce background noise when possible.
- Use captions when watching TV.
- Ask for repetition when needed.
- Choose well-lit environments for lip reading.
Families also benefit from these strategies. Our tips for communicating with hearing loss provide guidance for smoother conversations at home and in public.

The Importance of Professional Hearing Care
One of the most important steps in addressing conductive vs. sensorineural hearing loss is a thorough, in-person hearing evaluation. Many people delay testing because they assume hearing loss is a normal part of aging, or they think they can manage by simply turning up the TV volume. The truth is, a high-quality hearing test is the only way to understand what type of hearing loss you have and how severe it is. Without this information, treatment is often delayed or ineffective.
A professional evaluation goes far beyond the quick screenings you sometimes see at health fairs or pharmacies. A complete test measures your hearing across a range of frequencies, compares air and bone conduction, and includes speech recognition assessments. These details allow a hearing care provider to distinguish between conductive, sensorineural, and mixed hearing loss. You can learn more about what to expect in our guide all about hearing tests.
Provider Expertise
Equally important is the expertise of the provider administering the test. While online hearing screenings can be a helpful first step, they cannot replace an in-person consultation with a licensed hearing care provider. During a personal appointment, your provider examines your ear canal, evaluates your medical history, and explains how your hearing profile connects to your daily challenges. This hands-on approach ensures you receive accurate results and a treatment plan designed for your specific needs.
If cost is holding you back, you may be surprised to learn that you can often schedule a free hearing test near you. A no-cost evaluation provides the clarity you need to make informed decisions about your hearing health. Many people find peace of mind simply knowing the status of their hearing and what solutions are available.
Professional care also gives you access to guidance on technology, communication strategies, and insurance coverage. A trusted provider will explain your results in detail, recommend the most appropriate devices, and make sure you know how to use them effectively. This personal support is something online hearing aid sales or self-fitting devices cannot replicate.
By investing in a professional evaluation, you are taking the most important step toward better communication, stronger relationships, and a higher quality of life.
Take the Next Step Toward Better Hearing
Conductive vs. sensorineural hearing loss may sound technical, but knowing the difference is the first step toward treatment. Conductive loss often improves with medical care or bone conduction devices. Sensorineural loss is permanent but highly manageable with modern hearing aids and, when needed, cochlear implants. Both conditions benefit from professional evaluation and timely intervention.
Don’t let hearing loss hold you back. American Hearing + Audiology offers comprehensive testing, a wide selection of devices, and personalized care tailored to your needs. Find a convenient location near you and take the first step toward clearer hearing today. Contact American Hearing + Audiology.



