Understanding Ear Wax: How to Keep It in Check
We’re exploring ways to reduce ear wax through dietary choices and discussing foods that reduce ear wax. You’ll also learn techniques to massage ear wax out and when it’s time to seek professional ear wax cleaning. Stay tuned for actionable advice to keep your ears healthy.
What Is the Point of Ear Wax?
Ear wax, medically known as cerumen, plays a crucial role in maintaining ear health. It’s a complex substance comprised of cerumen from modified sweat glands, sebum, dead skin cells, and an organic composition that includes fatty acids, squalene, alcohols, and cholesterol.
Essential Functions of Ear Wax
- Skin Protection: Earwax safeguards the delicate skin of your ear canal, preventing it from drying out and becoming itchy.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: It assists in the removal of dead skin cells and other debris, ensuring that your ears remain clean.
- Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Fungal Shield: Earwax protects against bacteria, fungi, and other pathogens, reducing the risk of infections.
- Barrier Against Foreign Objects: Earwax acts as a filter by trapping dirt, dust, and particulate matter that try to enter your ear canal.
- Water-Resistant Lining: A waterproof barrier prevents water from entering and causing infection.
- Guarding the Eardrum: Earwax acts as a protective layer between the external environment and your sensitive eardrum.
While earwax serves multiple beneficial purposes, excessive production can lead to issues like ear blockages, hearing loss, and tinnitus. If you experience these symptoms, consider the following ways to reduce ear wax for effective relief.
But remember, a balanced amount of earwax contributes to overall ear health. So it’s often best to simply leave it alone.
What Are Some Common Causes of Ear Wax Buildup and Techniques to Remove It?
Understanding the factors contributing to ear wax buildup helps you take proactive measures for ear health. There can be many causes of ear wax buildup, including:
- Narrow or Hairy Ear Canals: More likely to trap earwax, impeding natural drainage.
- Overproduction of Earwax: Genetics, age, or other factors can cause some people to produce more earwax.
- Cotton Swabs: Push earwax deeper, leading to blockages.
- Hearing Aids: Trap earwax and hinder natural drainage.
- Medical Conditions: Eczema and psoriasis can trigger excessive earwax production.
- Lifestyle Factors: Frequent use of earplugs, earbuds, or other objects can cause buildup.
- Age: Earwax becomes drier with age, increasing the risk of impaction.
Symptoms of Ear Wax Buildup
Recognizing the signs of earwax buildup is crucial for timely intervention. Here are symptoms to be aware of:
- Earache: A dull, persistent pain inside your ear, often signaling a blockage.
- Tinnitus: Ringing, buzzing, or humming noises in the ear can indicate excessive earwax affecting auditory pathways.
- Itchiness: Irritation and itching inside the ear canal often accompany earwax buildup.
- Hearing Loss: Diminished hearing or a feeling of “fullness” in the ear may occur.
- Odor: A foul smell coming from the ear is a less common but noteworthy symptom.
- Dizziness: Excessive earwax can affect your balance, leading to episodes of dizziness.
- Cough: A buildup may trigger a reflex cough due to the shared nerves between the ear and the throat.
- Hearing Aid Malfunction: Excessive earwax can cause your hearing aids to work less effectively.
- Partial or Worsening Hearing Loss: Left untreated, earwax blockage can escalate to more significant hearing impairment.
If you notice any of these symptoms, call your local American Hearing + Audiology center for an appointment.
Learn more about the types of tinnitus and how to handle them.
Techniques to Reduce Ear Wax
- Limit Hearing Aid Use: Periodic breaks help prevent earwax accumulation.
- Ear Drops: Soften earwax so it falls out naturally.
- Massage Techniques: Help to move the wax out of the ear canal naturally.
- Professional methods: ear irrigation, micro-suction, and curette methods are ways that professionals can reduce ear wax.

What Not to Do About Ear Wax
Navigating earwax removal can be tricky, and some popular methods can worsen the situation or even cause harm. Here are the things to avoid:
- Cotton Swabs: Although commonly used, cotton swabs can push earwax further into your ear canal. The American Academy of Otolaryngology advises against using them for this purpose.
- Home Suction Devices: Products like Wax-Vac® aren’t generally effective, and most healthcare providers don’t recommend them.
- Ear Candles: Marketed as a natural earwax removal solution, ear candles are not only ineffective but risky. They can lead to external ear burns, ear canal injuries, or even eardrum perforation.
- Unverified DIY Methods: Other methods, such as vacuum kits, lack scientific backing and are less safe or effective than medical procedures.
If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, consult a healthcare provider or hearing specialist for professional guidance.
Understand more about how to protect your hearing.
How to Massage Ear Wax Out
Massaging your ears can temporarily relieve the discomfort associated with earwax buildup. Although not backed by formal research, many find it useful while awaiting professional treatment. Below is a step-by-step guide on massaging ear wax out effectively:
- Get Comfortable: Find a quiet and relaxing space to begin the massage. Sit or stand comfortably.
- Position Your Fingers: Place your pointer and middle fingers behind your earlobe, near the base of your ear.
- Start the Circular Motion: Press gently and make slow, circular movements. This helps to dislodge the earwax from the walls of the ear canal.
- Add Earlobe Tugging: Gently tug on your earlobe while simultaneously opening and closing your mouth. This motion can facilitate further loosening of the earwax.
- Tilt Your Head: As you massage, tip your head slightly to the side to encourage the loosened wax to drain out.
- Repeat as Necessary: Perform these steps for both ears, taking care not to exert too much pressure.
- Note on Timing: Limit the massage to a few minutes per ear to avoid irritation.
- Seek Professional Help: If the issue persists or worsens, consult a healthcare provider for an appropriate treatment plan.
While you can learn how to massage ear wax out, and massaging may provide some relief, it’s not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Always consult a hearing care professional for persistent or severe symptoms.
What Are Some Foods That Reduce Ear Wax?
While no specific foods have scientific backing to directly reduce earwax, a balanced diet can support ear health and may indirectly help manage earwax levels. Below are some foods and lifestyle tips that may contribute to healthier ear canals.
Nutrients for Ear Health
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna, Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that could minimize inflammation in the ear canals.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Loaded with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits and vegetables like oranges, spinach, and sweet potatoes may protect ear canals from oxidative damage.
- Whole Grains: Rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals such as zinc, whole grains support digestive and ear health.
- Vitamins A, C, and E: These vitamins boost the immune system and may help to decrease inflammation. Foods rich in these vitamins include nuts, sweet potatoes, and spinach.
- Zinc: Essential for ear health, zinc is found in foods like legumes, nuts, and whole grains.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking ample water helps soften hardened earwax and prevents the ear canal from drying out, which can lead to excess wax production.
So while there aren’t specific foods that reduce ear wax, a balanced diet can contribute to healthier ears. For persistent issues, consult a hearing care provider for professional removal.
Get more hearing health questions answered.
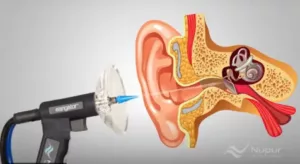
Visit an American Hearing and Audiology Center for Professional Ear Wax Removal: Spotlight on the Earigator
When you’re dealing with persistent earwax buildup, a visit to an American Hearing and Audiology Center could be the solution you need. With cutting-edge Earigator technology and skilled audiologists, you can expect a thorough and comfortable experience. Here’s what you need to know.
Pre-Appointment Steps
Upon arrival, you’ll discuss your symptoms with an audiologist or hearing professional. If you’re a new patient, they will also collect information on your medical and health history. An initial visual examination using an otoscope helps confirm the presence of earwax buildup.
Time Expectations
The duration of the earwax removal appointment generally ranges from 15 to 30 minutes. However, larger buildups might require a more extended session, potentially using multiple removal methods. The process could be as quick as 15 minutes for small buildups or repeat visits.
Ear Wax Removal Methods
Audiologists typically employ two primary methods:
- Manual Method: A curette or small tool removes the earwax. Alternatively, suction or forceps might be used. A video otoscope provides the audiologist with a clear view of the ear canal.
- Irrigation Method: A water-filled syringe softens and flushes out the earwax.
Sometimes, both methods are used in a single appointment, depending on the earwax’s size and consistency.
The Earigator Advantage
The Earigator is a revolutionary tool available at all our locations. Designed by an Otologist, this equipment combines the functions of an otoscope and irrigation, offering an advanced approach to earwax removal. Here’s why the Earigator stands out:
- Comfort: Unlike traditional metal tools, the Earigator ensures a less painful experience, minimizing the risk of bleeding.
- Efficiency: Nurses and clinicians can safely remove even the most stubborn earwax.
- Temperature Control: The Earigator maintains water at body temperature, avoiding any discomfort or vertigo.
- Pressure Controls: Optimized settings ensure quick and safe earwax removal without endangering the eardrum.
Persistent symptoms such as hearing loss, tinnitus, or discomfort warrant a professional consultation. The American Hearing and Audiology Centers provide a safe and advanced alternative for earwax removal with the Earigator technology. Please schedule an appointment with American Hearing + Audiology if you’re concerned about your ear wax.






